Call options
A call option contract gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy an asset at a specific price on or before a specific date.
Example of how it works
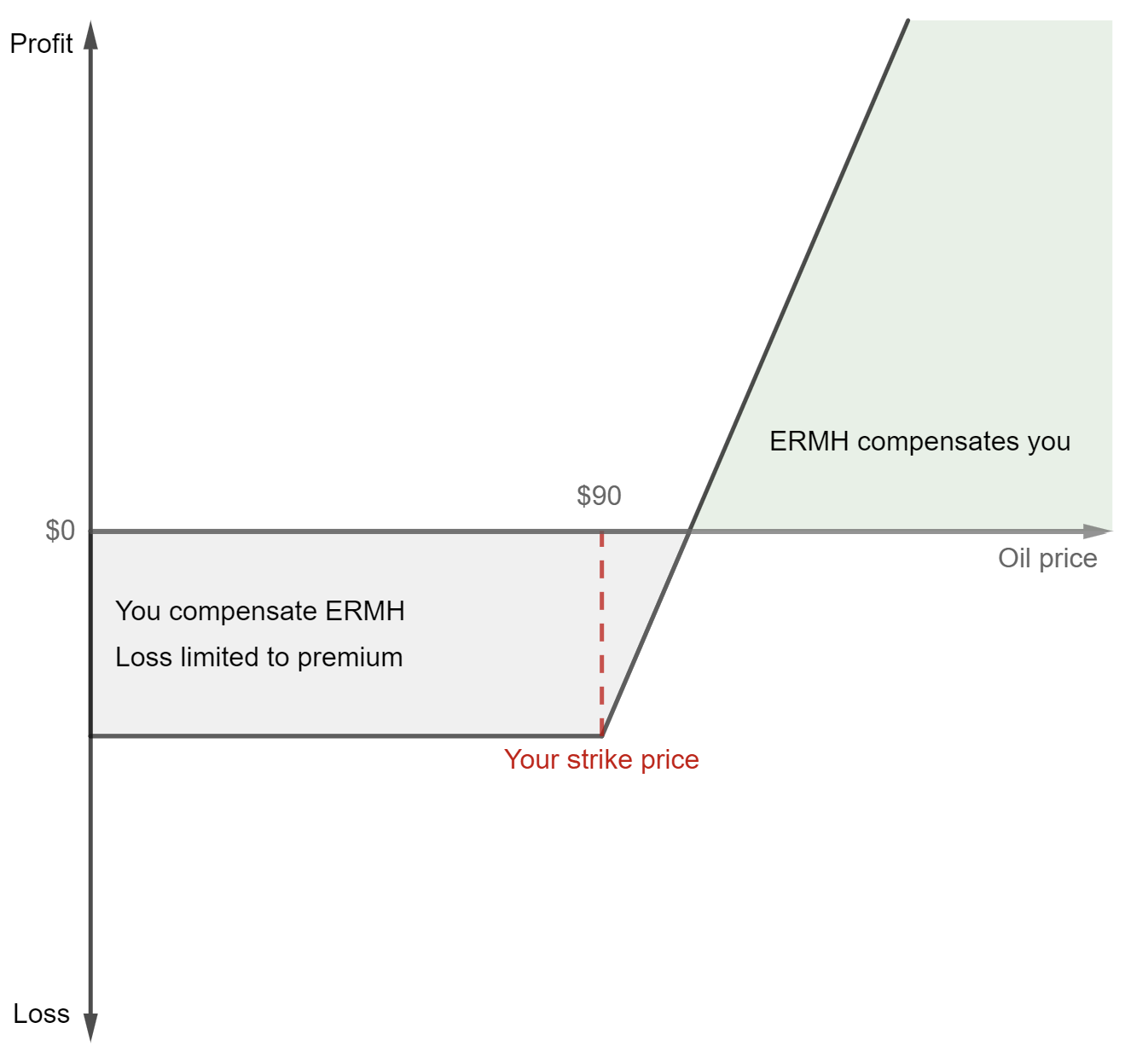
You buy call options with a strike price of $90 per barrrel.
Scenario 1 – Oil prices increase: The price of oil rises to $100 per barrel. Due to your call options, you have the right to buy barrels of oil at the lower strike price of $90 per barrel. This allows you to purchase the oil below the current market price and benefit from the price difference.
Scenario 2 – Oil prices decline: The price of oil decline to $80 per barrel. In this case, since the market price is lower than the strike price of $90 per barrel. You let the options expire worthless, and your loss is limited to the premium you paid for purchasing the options.
Before you open your financial hedging position, you first need to agree upon the floowing things:
⇒ A period for your hedging (E.g. six months)
⇒ A hedging volume for each month
⇒ The product that should be hedged
⇒ The trading currency (EUR, DKK, GBP, USD or contact for others)
⇒ A fixed price
ADVANTAGES AND RISKS
↑ Protection against a increase in prices
↑ Creates predictability for your bottom line
↑ Potential upside if prices increase
↓ No benefits from decreasing prices
Let us secure your bottom line
We are ready to assist with risk management of all kinds of energy products and services, so if your company’s budget is affected by energy price fluctuations, don’t hesitate to contact us!